How to Choose the Right Security Vendors for Your MSP Stack
Are you frustrated with how many vendors there are for so few MSPs?
Vendor marketing is often vague and confusing, leaving many MSPs wondering:
You’re not alone. Use this guide to help you.
Navigate Vendor Relationships
Myth: Vendors solve security problems.
Fact: Vendors provide tools and resources to support your cybersecurity efforts.
Don’t enter a vendor relationship based on buzzwords and promises to solve “all of your security problems.”
Enter the relationship with the understanding that no vendor can solve all of your security challenges- they are merely there to support your efforts in the specific areas they are experts in.

So, with plenty of vendors in the sea, how do you know which is right for you?
Cyber Defense Matrix
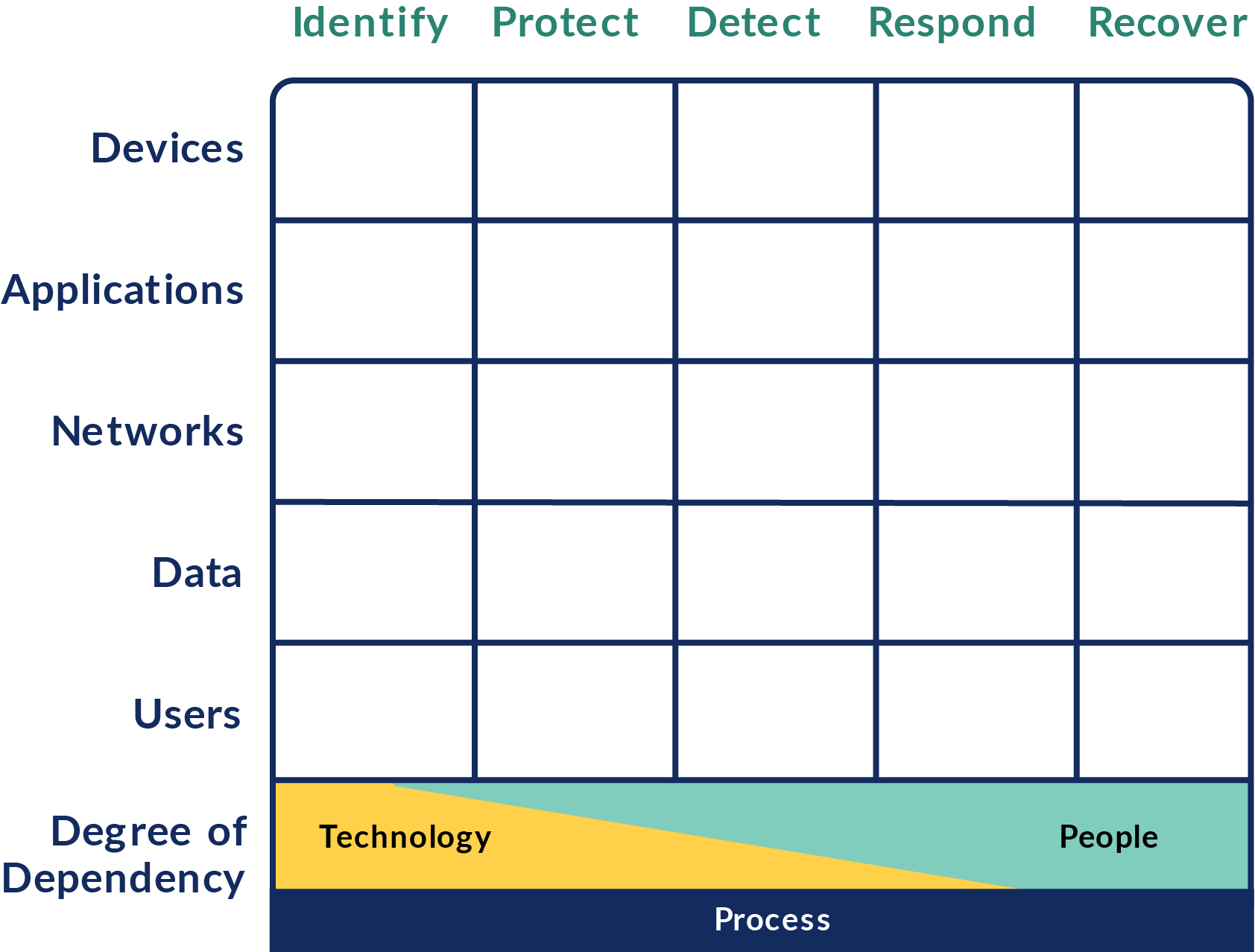
The matrix is a powerfully simple and effective way to understand the vendor ecosystem and understand what tools fill what areas of need.
It was created by Sounil Yu.
When Sounil was Head of Innovation at Bank of America, vendors constantly reached out to him for a demo hoping for a multi-million dollar deal.
Necessity is the mother of invention, so Sounil created the matrix directly mapped to the Cybersecurity Framework. It was ground breaking yet elegant and simple.
The Cyber Defense Matrix has been one of the most powerful cybersecurity revelations for many MSPs.
You can directly map your tools into the Cyber Defense Matrix.
This will help your MSP with the following:
- Stack Analysis
- Strategizing
- Budgeting
- Sales Conversations
As you map out your tools, a few things will stand out to you...

You can now ask vendors insightful questions like:
“Where exactly do you fit best into the cyber defense matrix?”
“Can you clarify why?”
Note: Each tool can only fit into one primary category.


You may have gaps.
There are certain areas of the Cyber Defense Matrix where there are no tools. This might be an opportunity for you to address a gap or you may simply have to accept the gap.
Note: The Respond and Recover columns usually have many gaps because they tend to be more people and process driven than tool driven.
There may be overlap.
Sometimes this is necessary. Sometimes you may have the need for multiple tools depending on the architecture of your environment, or cloud vs. on-prem or simply because correctly filling an area in the Cyber Defense Matrix requires multiple tools to accomplish it completely.
.png)
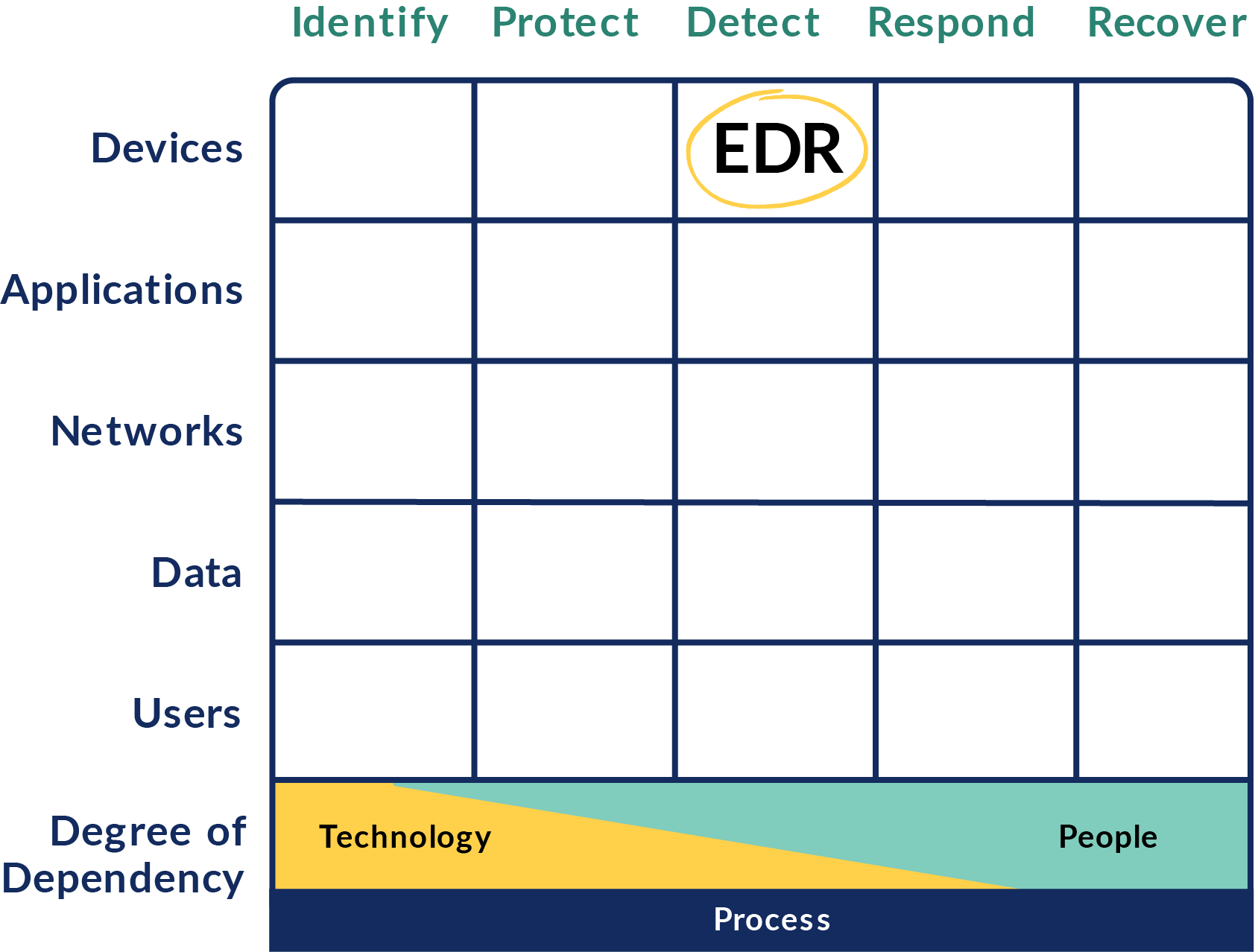
How to Map Your Tools
Example:
Take an EDR.
Its primary capability is to detect threats on end points like laptops or desktops. As a result, an EDR would go in the Detect column primarily under the Devices row.


But why the increased need for security vendors, anyway?
Meet Cyber Insurance Requirements
Cyber Insurance has been the top driver for security investment among clients over the past two years.
Cyber carriers require a minimum standard of security before they agree to shoulder the cyber risk of a client.


Need more info on cyber insurance?
A breach can easily cost $500K to $1M+, even for small businesses.
For cyber carriers to take on that risk, they’ve started mandating security requirements that have proven to reduce the occurrence and cost of a breach. These have been determined based on carriers’ up-close experience with both the volume of security incidents as well as the internal details that cause breaches to occur.
Some potential costs of a breach:
- Ransoms
- Lost business
- Restoration of services
- Digital forensics
- Legal action
- Regulatory action
There are five major requirements standardized by nearly all carriers.
Let's dive in.
1
Multi-Factor Authentication
All clients need MFA from the CEO down. Period.Carriers stand firm on this and not having MFA inplace could deem your MSP as negligent.
MFA stops over 99.9% of authentication attacks.
2
Segregated Backups
These are data backups separate from where the information is stored initially. Hackers have started to hunt for and destroy backups as part of their standard plan, so if backups are not separate, a ransom ware event could encrypt those backups, making them useless.
Separated backups are often cloud-based, but different servers are also utilized.

3
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR has become the defacto standard for endpoint security. It goes far beyond the capabilities of AV and gives deep insights into the activity and behavior of the endpoint. Carriers are now shifting to not just EDR in place but fully-managed 24/7 monitored EDR as well.
4
Vulnerability Scanning
Carriers are weary of paying out on claims when a company simply failed to patch against a known vulnerability. As a result, it’s become more common to mandate that clients scan their networks for the presence of vulnerabilities.
Most carriers are asking clients to remediate and patch all high and critical risk vulnerabilities within 30 days.
5
Security Awareness Training & Phishing Simulations
Carriers realize that end users are both the weakest link and the most important asset when it comes to cybersecurity. While unknown vulnerabilities (called 0 Days) are always an issue, the majority of cyber incidents occur when employees are involved.
74% of all breaches include the human element.

.png)
Opening and clicking a link in a phishing email, falling for a scam, or visiting a compromised website are some of the most common entry points for cyberattacks.
Can you guess what the antidote is for all of these attack vectors? A well-informed workplace that understands the threat of cyber attackers.
This e-guide is brought to you by Phin
Breathe easy with Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulations that save you time, reduce headaches, and meet your cyber insurance requirements.
Hint for your defense matrix:
Phishing simulations are User/Identify
SAT is User/Protect

Written partnership with Wes Spencer, a cybersecurity expert and co-founder of Empath and Perch Security.

Want to learn more about the Cyber Defense Matrix?

